
Service hotline:
13533607738
18602592233
Welcome to 广东脊祥万岁健康管理有限公司!
最新资讯
Enteritis, hepatitis, gastritis, pancreatitis... Inflammatory diseases are not uncommon in life. You must be curious, how far is inflammation from cancer?
Inflammation, sometimes an accomplice to cancer
Medically, cancer refers to malignant tumors; inflammation refers to the body's response to tissue and cell damage. On the surface, there seems to be little relationship between the two.
However, recent studies have shown that:
About one fifth of cancer patients have long-term chronic inflammatory stimuli.
Four-fifths of cancer patients could not find the background of chronic inflammation. However, inflammatory cells infiltrated into their cancer tissues.
In short, inflammation can sometimes be an accomplice of cancer and a possible cause of cancer, while inflammation can sometimes be a concomitant phenomenon of cancer.
Not all enteritis cancers, but chronic ulcerative colitis is widely believed to be associated with an increased risk of malignant tumors. Many people with ulcerative colitis do not pay enough attention to inflammation. They take anti-inflammatory drugs when they get sick. As a result, the symptoms of ulcerative colitis are not cured. It can easily lead to repeated attacks, from mild to severe, and even eventually to canceration.
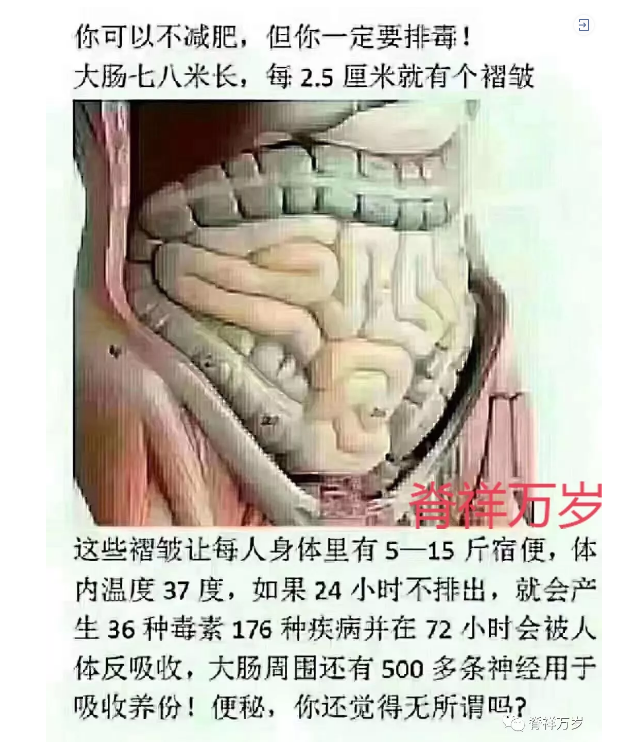
1.Symptoms of digestive tract in 30-40 years old and over.
2. Have a history of colorectal cancer。
3. There are precancerous lesions of large intestine, such as adenoma, ulcerative colitis and schistosomiasis.
4. Family history of cancer, family polyposis, hereditary colon disease.
5. History of pelvic radiotherapy.
6. History of cholecystectomy or appendectomy.
7. People who often eat high-fat and high-heat food, live irregularly, smoke and drink, and have the habit of staying up late.
Hepatitis Cirrhosis Hepatocellular Carcinoma

Hepatitis increases the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Chronic viral hepatitis such as hepatitis B and hepatitis C is an important cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. Continuous replication of the virus in the liver causes chronic damage to the liver. If we do not pay attention to treatment, it may lead to cirrhosis for a long time. If cirrhosis is not treated in time, it may deteriorate into hepatocellular carcinoma.
According to the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the risk groups of HCC are generally divided into three categories:
1. The first group is the high-risk group, such as patients with cirrhosis due to chronic viral hepatitis (hepatitis B or hepatitis C).
2. The second group is at moderate risk, such as patients with chronic viral hepatitis, but without a family history of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma.
3. The third group is low-risk population, such as patients with cirrhosis caused by non-viral causes.

Helicobacter pylori can cause gastritis and peptic ulcer, and then develop into gastric cancer. WHO classifies Helicobacter pylori as a carcinogen, which can be transmitted by hand, dirty food, dirty tableware and feces.

1. People aged 50 to 60. This is the high incidence age of gastric cancer, people in this age group should pay attention to stomach discomfort.
2.The incidence of Helicobacter pylori infection, especially in children with Helicobacter pylori infection, will increase by 3 to 5 times.
3. The incidence of gastric cancer in the family, especially in the offspring of immediate relatives, will increase by 2-3 times.
4.People who drink and smoke for a long time are at high risk of gastric cancer.
5. Lack of vitamin A, vitamin C, vitamin E, and people who like to eat fermented and fumigated foods have a significantly increased risk of gastric cancer.

Not all cervicitis is cancerous. Cervical inflammation caused by HPV infection may develop into cervical cancer in 8-10 years without treatment. The cervicitis caused by gonococcus and Chlamydia will not develop into cervical cancer.
However, it also reminds women friends that they should pay attention to hygiene problems in peacetime, use clean underwear, sanitary napkins, etc. It is best to receive regular screening for cervical cancer.
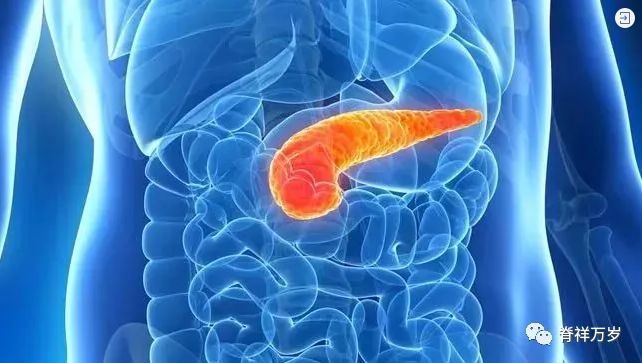
80% of pancreatic cancer patients have a history of pancreatitis. Generally speaking, if acute pancreatitis occurs repeatedly and is not well treated, it is easy to develop into chronic pancreatitis, which increases the risk of pancreatic cancer.
Reasonable diet is very important to prevent pancreatitis. Alcohol abuse and overeating are the "killers" of pancreatitis, which should be avoided as much as possible.
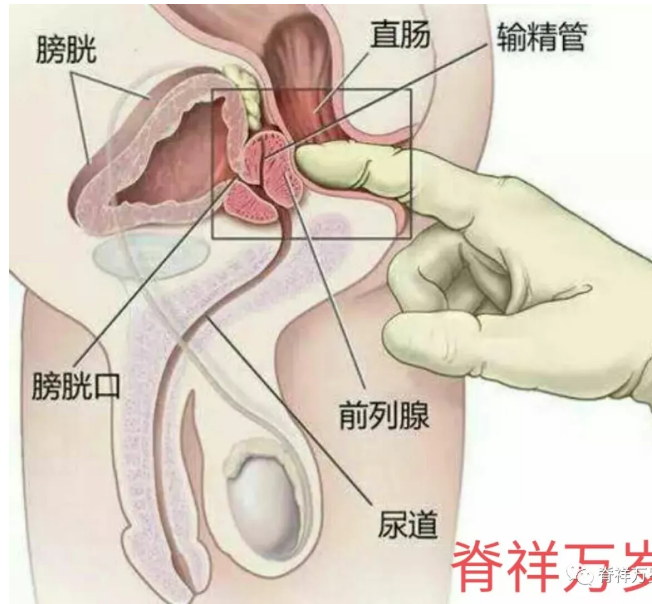
There is no doubt that prostatitis is a common disease in adult males, but it is far from canceration. Although long-term stimulation of chronic inflammation may turn into cancer, some research data show that the incidence of prostate cancer in patients with chronic prostatitis is higher than that in the general population, so patients with chronic prostatitis need not worry about the psychological burden of canceration.
Male friends must pay attention to drinking water, do not suffocate urine, pay attention to keeping warm to prevent cold, as far as possible to avoid sedentary behavior.
Not all breast diseases can be related to breast cancer. Generally speaking, non-proliferative lesions are not closely related to the occurrence of breast cancer, such as some breast cysts, mastitis, nipple discharge, etc. Mastitis is common in breast-feeding period after childbirth, which is caused by improper handling of breast-feeding. But non-breast-feeding period will also appear mastitis, it is best to pay attention to, not timely treatment is easy to damage the breast, may increase the risk of canceration.。
It is suggested that women should change their underwear frequently and not wash them together. It is better to use less washing machine to wash underwear.

Some patients with chronic pharyngitis worry that repeated pharyngitis can cause cancer. In fact, there is no need to worry about the possibility of chronic laryngitis progressing to cancer is extremely small, almost "parallel" two lines, it is difficult to cross. But this can not be an excuse for not paying attention to pharyngitis.
However, the early symptoms of some tumors are similar to those of chronic pharyngitis, such as hypopharyngeal cancer such as nasopharynx and oropharynx.
Inflammation is sometimes the "accomplice" of cancer
But not all inflammation is cancerous.
Don't be afraid of inflammation
Inflammation reminds us to pay attention to the body
Start at every point of life