
Service hotline:
13533607738
18602592233
Welcome to 广东脊祥万岁健康管理有限公司!
最新资讯
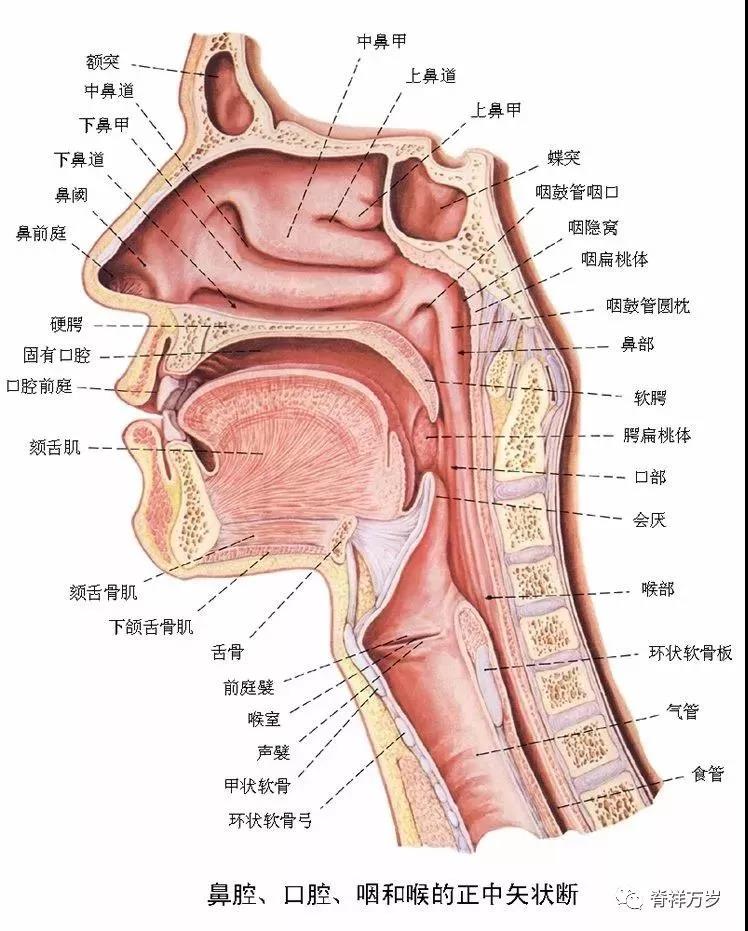
nasal cavity
The nasal cavity is an irregular cavity surrounded by bone and cartilage and covered with mucosa and skin. The nasal cavity is divided into left and right cavities by the middle nasal diaphragm. It opens to the outside through the nostril in the front and to the pharynx through the posterior nostril in the back. Each side of the nasal cavity is divided into anterior and posterior parts, the anterior nasal vestibule and the posterior nasal cavity.
The hollow space surrounded by the nose wing is lined with skin and has thick nasal hair, which has the function of filtering dust. Because of the lack of subcutaneous tissue in this area, the pain is more severe when boils occur.
As the main part of the nasal cavity, it is often referred to as the nasal cavity in clinic. It is composed of bone nasal cavity covered with mucosa. The upper, middle and inferior turbinates can be seen on the lateral wall, and the upper, middle and inferior nasal meatus formed under each turbinate respectively. The medial and lateral wall of the nasal cavity is the nasal septum, which is composed of osseous nasal septum and nasal septum cartilage covered with mucosa.
The mucosa of the innate nasal cavity can be divided into the olfactory part and the respiratory part. The olfactory part is located in the upper turbinate and the nasal septum opposite to the upper turbinate. The mucosa contains olfactory cells, which can sense olfactory stimulation; the respiratory part is the part outside the olfactory part, which is rich in blood vessels, mucous glands and cilia, which can adjust the temperature and humidity of inhaled air; and purify bacteria and dust.
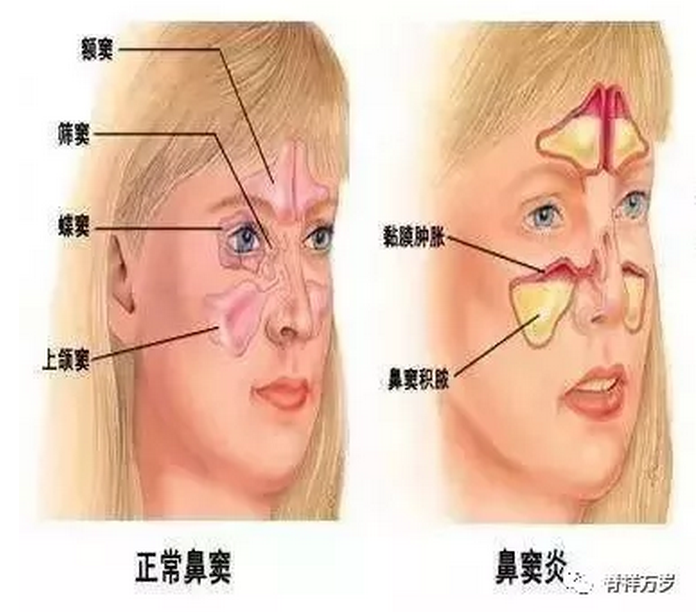

Paranasal sinuses
Paranasal sinuses, also known as paranasal sinuses, are made of bone paranasal sinuses lined with mucosa. There are four pairs of paranasal sinuses, all of which open in the nasal cavity. The anterior and middle atria of maxillary sinus, frontal sinus and ethmoid sinus open to the middle nasal meatus; the posterior atrium of ethmoid sinus opens to the upper nasal meatus; and the sphenoid sinus opens to the posterior and upper part of the upper turbinate. Because paranasal sinus mucosa is connected with nasal mucosa, it can spread to paranasal sinus and cause paranasal sinusitis when nasal cavity is inflamed. The opening of the maxillary sinus is higher than the base of the sinus, so when the maxillary sinus is inflamed and purulent, the drainage is often not smooth, resulting in sinus empyema. Paranasal sinus can adjust the temperature and humidity of inhaled air and resonate with pronunciation.
1. The maxillary sinus is located in the maxillary body, which is the largest volume in the sinus, averaging about 13 ml. The upper wall is the orbital floor. The bottom wall is alveolar process, which is closely related to the maxillary second bicuspid teeth (sometimes up to canines) and the first and second molars. The inner wall is part of the external wall of the nasal cavity, and the orifice of the sinus opens to the middle nasal meatus. The orifice of the sinus is higher, which is not conducive to drainage.
2. The ethmoid sinus is situated in the ethmoid bone above the nasal cavity, which is hive-like. There are about 3-15 ethmoid cells on each side. They were divided into two groups: the anterior group opened to the middle nasal meatus and the posterior group opened to the upper nasal meatus. The outer wall has paper pattern and tear plate bone separated from the orbital contents, and the wall is as thin as paper. The inner wall corresponds to the upper and middle turbinates of the inner wall of the nasal cavity. The inferior wall is a cribriform vesicle located in the middle nasal meatus. The parietal wall is part of the basal wall of the frontal sinus or the anterior cranial fossa. The anterior wall connects with the frontal process of the maxilla and the frontal sinus. The posterior wall can reach the anterior wall of sphenoid sinus.
3. The anterior wall of frontal sinus is the outer plate of frontal bone, which is thicker and contains bone marrow. The posterior wall is the inner frontal plate through which blood vessels enter the dura mater. The base is the orbital apex and the top of the anterior ethmoid sinus. The frontal sinus openings in the medial part of the basal wall lead to the front of the middle nasal meatus through the nasofrontal canal. The medial wall is bilateral frontal sinus septum.
4. There is an optic foramen at the angle between the parietal wall and the lateral wall of sphenoid sinus. The lateral wall is separated from the middle cranial fossa. The posterior wall is sphenoid body. The anterior wall of the sphenoid sinus opens naturally into the sphenoethmoid recess. The inferior wall is the posterior nostril and the top of nasopharynx.
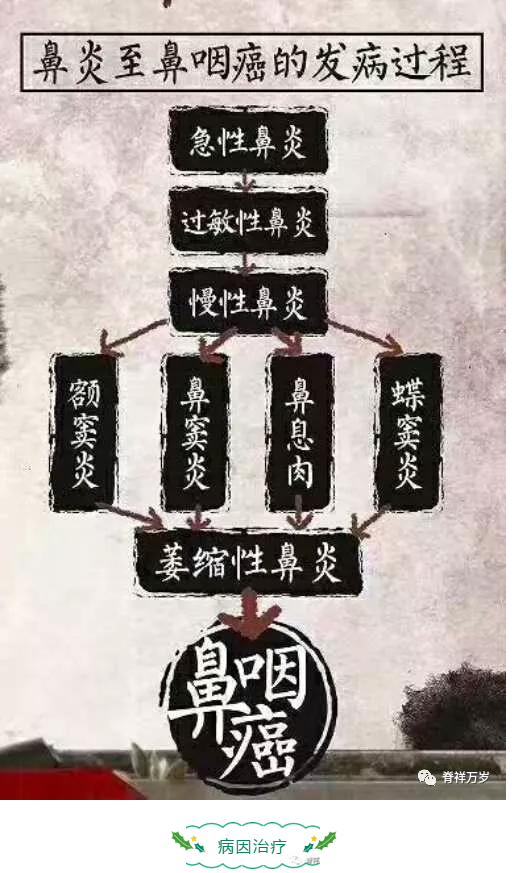
①Hypertrophic rhinitis
Persistent nasal obstruction is often severe, with few runny nose and mucous or pus. It usually has different degrees of headache, dizziness and loss of sense of smell.
②Rhinallergosis
The degree of nasal obstruction varies from mild to severe and often occurs abruptly. Runny nose is sparse and plentiful, often accompanied by itching and frequent sneezing.
③Vasomotor rhinitis
Symptoms are similar to variant rhinitis, with sudden onset and rapid subsidence. There are obvious inducing factors.
④influenza
Systemic symptoms are severe, such as high fever, chills, headache, aches and pains in joints and muscles. The symptoms of upper respiratory tract were not obvious.
⑤Acute infectious diseases
Some acute respiratory infectious diseases, such as measles, scarlet fever, pertussis and other early symptoms of acute rhinitis can occur. In addition to acute rhinitis, these diseases also have their own manifestations of the disease, and severe systemic symptoms, such as high fever, chills, headache, muscle soreness and so on. It can be distinguished by detailed physical examination and close observation of the course of the disease.
⑥Nasal diphtheria
Children patients should pay attention to differentiating the disease. Nasal diphtheria is characterized by haemorrhage, severe systemic symptoms, and often accompanied by pharyngeal diphtheria.

1.Acute sinusitis
Inflammation of the nasal cavity spreads through the opening of the sinus to the sinus, causing acute suppurative sinusitis, of which maxillary sinusitis and ethmoid sinusitis are common.
2、Acute otitis media
The infection spread to the middle ear through the eustachian tube.
3、Acute pharyngitis, laryngitis, tracheitis and bronchitis
The infection spread downward through the nasopharynx. Pneumonia can also occur in children, the elderly and those with low resistance.
4、Nasal vestibulitis
The infection spreads directly forward.
5、Other infections
Diffusion through nasolacrimal duct can also cause ocular complications, such as conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, etc。
Rhinitis Bacteriostasis Ointment,For: allergic rhinitis, sinusitis, acute, chronic rhinitis, and snoring caused by very good effect.
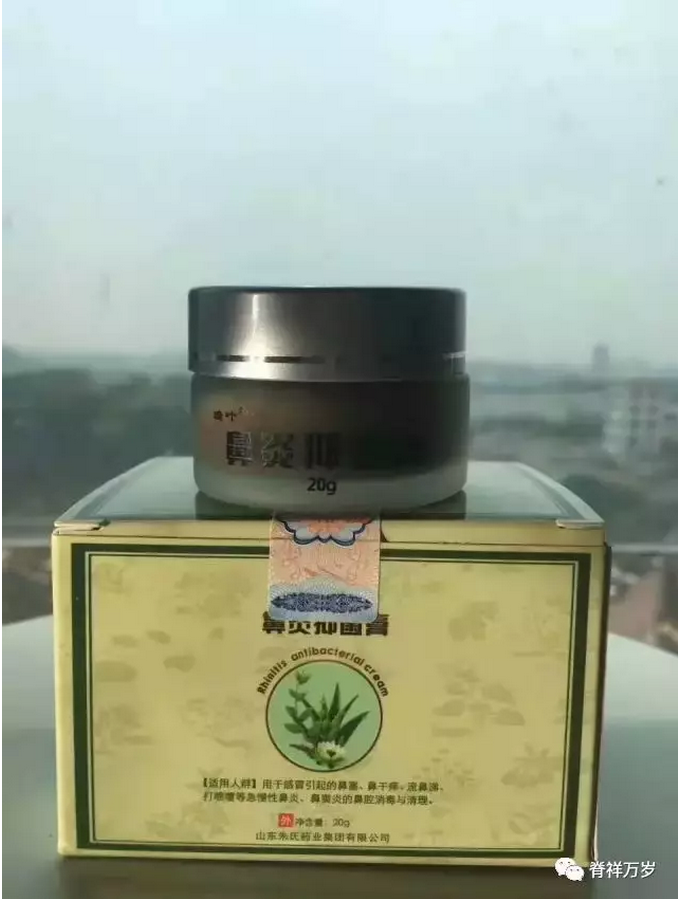

Pure Chinese herbal formula of rhinitis bacteriostasis ointment,
No hormones, antibiotics and corrosive drugs, safer and more effective. Xanthium sibiricum, geese do not eat grass, honeysuckle, borneol, play
Clearing heat and detoxification, relieving swelling and pain, promoting blood circulation and promoting orifice, clearing nasal purulent secretions. For all kinds of rhinitis, sinusitis, mixed rhinitis caused by nasal obstruction, runny nose, headache, tinnitus, eye astringency, memory loss, sneezing and so on.
Method of using antimicrobial ointment for medicinal rhinitis:
1.Suggestions to seize up congestion, see what nature of the other party's rhinitis, generally allergic rhinitis is the majority, we recommend congestion nasal concha, because hospitals can not find the upper and lower turbinates, we can plug the nasal concha after not much effect, we plug the inferior turbinate.
2.Most of the rhinitis patients with habitual runny nose are due to the severe cold in the body. We usually let him eat something important to dispel the cold, which is more conducive to the treatment of rhinitis.
3.Stick to the trial for 15 days to about a month. The nasal cavity can be repaired in time according to the situation. Severe rhinitis is treated for 2 to 4 courses.
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis:
Symptoms of allergic rhinitis include itching, sneezing, runny nose and blocked nose. In addition, allergic rhinitis of different syndromes has its special clinical manifestations.
Symptoms of chronic rhinitis and sinusitis
Symptoms of chronic sinusitis 1: recurrent sensory headache
This is a common symptom of chronic sinusitis. For chronic suppurative sinusitis, there will be obvious local pain or headache, often manifested as blunt pain or heavy head feeling, heavy during the day and light at night. Sinusitis mostly manifested as frontal and nasal root swelling or frowning pain, headache of sinusitis in the top of the head, temporal or occipital region.
Symptoms of sinusitis 2: Frequent nasal obstruction
This is a common symptom of chronic sinusitis. For chronic suppurative sinusitis, there will be obvious local pain or headache, often manifested as blunt pain or heavy head feeling, heavy during the day and light at night. Sinusitis mostly manifested as frontal and nasal root swelling or frowning pain, headache of sinusitis in the top of the head, temporal or occipital region.