
Service hotline:
13533607738
18602592233
Welcome to 广东脊祥万岁健康管理有限公司!
最新资讯
Rhinitis and sinusitis, whether acute or chronic, may cause some of the following complications, whether for adults or children. However, due to the physiological and pathological characteristics of children, the impact of rhinitis and sinusitis on children is more significant and more common, so it is also more important and needs to be paid enough attention. Although the following is mainly about children, the impact on adults can also be referred to.

What is rhinitis and sinusitis in children
Children's rhinitis, mainly refers to children's acute rhinitis and chronic rhinitis. The nose belongs to a part of the upper respiratory tract. When acute rhinitis occurs, it is called cold in traditional Chinese medicine, upper respiratory tract infection in Western medicine, and acute rhinitis in otorhinolaryngology. Acute rhinitis is a part of upper respiratory tract infection, which may be accompanied by acute pharyngitis, acute laryngitis and other pathological changes. Chronic rhinitis is chronic inflammation of nasal mucosa. Whether it is acute rhinitis or chronic rhinitis, it can cause nasal swelling and nasal obstruction; it can cause nasal endocrine secretion to increase and cause bleeding or runny nose.

Children's sinusitis, acute and chronic, refers to children's sinus mucosa and submucosal tissue suppurative inflammation, often caused or accompanied by nasal mucosal inflammation, also known as nasal-sinusitis.
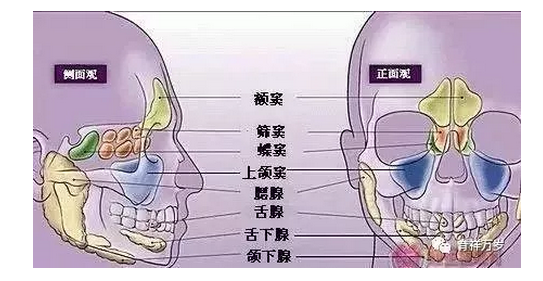
Paranasal sinuses, also known as paranasal sinuses, are sinus cavities within the skull, each opening to the nasal cavity. At least 8 sinuses (maxillary sinus, frontal sinus, ethmoid sinus, sphenoid sinus) are located on the left and right sides of the nose, named after the skull. The maxillary sinus is the largest, located in the maxillary bone on both sides of the nose, under the orbit and inside the zygoma. According to the development of children, maxilla has been formed at birth and its sinus cavity is larger; ethmoid sinusitis may occur after 2 years old, frontal sinusitis may occur after 10 years old, and sphenoid sinusitis may occur in older children. Therefore, maxillary sinusitis is the most common disease in clinic, and it is not uncommon for older children to have multiple sinusitis in succession or at the same time.
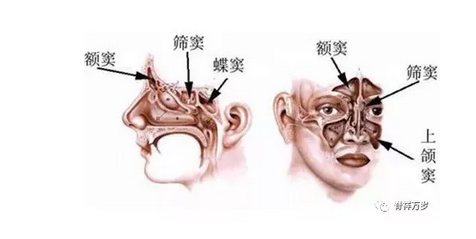
What are the hazards of rhinitis and sinusitis in children
Acute rhinitis, acute sinusitis, chronic rhinitis and chronic sinusitis in children, especially chronic sinusitis for a long time, can easily cause many complications. The main reason is that inflammation extends directly to adjacent tissues and organs, such as nasal, jaw and eye inflammation.
Secondly, the symptoms of the throat, lungs and lower respiratory tract, middle ear, digestive system, and mental nervous system are caused by the backflow of runny nose or ingestion into the stomach.
Why is rhinitis and sinusitis more harmful to children?
Because children are delicate and inflammation is often strong. When acute rhinitis and sinusitis occur, the nasal mucosa is prone to high edema and polypoid degeneration, which makes the disease more serious and develops faster than adults. Especially acute suppurative inflammation may also infect the surrounding area, causing eye and jaw complications.
Because children will not mainly rule out runny nose, the runny nose is more serious than adults, which is easy to cause otitis media, throat inflammation and lower respiratory diseases; inflammatory secretions are easy to swallow into the stomach, resulting in the absorption of bacteria and toxins, more likely than adults to produce digestive tract symptoms (poor appetite, diarrhea, constipation, abdominal pain, etc.); if it is chronic rhinopathy, it is easy to cause mental nervous system. Symptoms (night airing, restlessness of sleep, molars, hyperactivity, mental retardation, etc.); long-term digestive disorders and poor nutrition, easy to cause children's development disorders (yellowish, thin, short stature, etc.). Therefore, children's rhinitis and sinusitis are more harmful than adults.

What are the common complications of rhinitis and sinusitis in children
1. Allergic rhinitis and chronic rhinitis
Allergic rhinitis can cause or aggravate sinusitis; when sinusitis occurs, physical resistance decreases, and in some patients, increased nasal sensitivity changes may occur, leading to or aggravating allergic rhinitis. And sinus inflammation, pus to the nasal cavity outflow, will inevitably cause rhinitis. Therefore, chronic sinusitis is often accompanied by chronic rhinitis. Therefore, in the presence of both sinusitis and chronic rhinitis, the treatment of sinusitis is the main.
2. nasal polyps
The nasal mucosal edema caused by inflammation may cause polypoid change of nasal concha or nasal cavity polyp or sinus polyp. Polyps in nasal cavity are easy to obstruct, which makes sinusitis difficult to cure and allergic rhinitis difficult to cure. It is necessary to cancel the measures of removing nasal polyps in order to better treat sinusitis and allergic rhinitis.
3. Olfactory disorders
Children often do not complain. Olfactory disorders can occur in older children or adults with chronic sinusitis. The olfactory disturbance caused by acute sinusitis is irrelevant. When sinusitis improves or recovers, normal olfaction will be restored. Long-term chronic sinusitis can cause respiratory obstructive olfactory dysfunction due to nasal obstruction, but it is not important. It may also be caused by inflammation of nasal olfactory mucosa, resulting in peripheral neurosensory olfactory dysfunction, which requires specific treatment.

1. Can cause dacryocystitis, conjunctivitis
Inflammation is mainly caused by eye infection through nasolacrimal duct. In the treatment of rhinopathy, it is necessary to cooperate with ophthalmological treatment, or vice versa, with rhinological treatment in the treatment of ophthalmopathy.
2. Optic neuritis
The eye (spherical, known as the "eyeball") is located in the orbit. The optic nerve enters the eye in the orbital fissure behind the eyeball. The fissure behind the eyeball is closely adjacent to the nasal sinus (mainly the "ethmoid sinus"). When ethmoid sinus inflammation occurs, inflammation may invade the site, leading to the occurrence of optic neuritis, so that patients'vision rapidly declines in the short term. Ophthalmological treatment is needed in the treatment of sinusitis.
3. intraorbital infection
That is intraorbital infection. The orbit is close to several sinuses. Inflammation of the sinuses may enter the orbit and cause intraorbital infection with serious consequences.
4. Intracranial infection
The sinuses themselves grow in the skull, which encloses the soft tissue of the brain. If the sinus inflammation penetrates the skull, it enters the skull, causing inflammation of the brain soft tissue, with serious consequences and even endangering life. Fortunately, the incidence of this situation is not high, but it is never possible.
Otitis media is easily complicated, including suppurative otitis media and non-suppurative otitis media. There may be three reasons why rhinitis and sinusitis can cause otitis media.
First, when nasal inflammation occurs, a large number of bacterial secretions (pus, mucus) often flow out. If nasal secretions flow backward, they enter the nasopharynx (the junction of the nose and pharynx), which can cause nasopharyngeal inflammation. If the inflammation of the nasopharynx causes congestion and swelling of the mucosa here, it will block the opening of the middle ear canal to the nasopharynx (hereinafter referred to as the eustachian tube eustachian orifice) and cause exudative otitis media; if bacteria enter the middle ear cavity along this orifice (eustachian tube), it may be possible. Causes suppurative otitis media.
Second, when sinusitis occurs, it is necessary to blow your nose regularly. If the method of blowing the nose is not correct, it will make the nose pour into the nasopharynx, further occur the above situation, causing otitis media.
Thirdly, when chronic sinusitis occurs, the resistance of the body often decreases. When nasal secretions enter the nasopharynx and middle ear cavity, it is easy to make inflammation develop and cause otitis media. The view of traditional Chinese medicine is that "insufficient vital energy makes pathogenic toxins vulnerable to invasion".
Inflammatory secretions (runny nose) flow backwards into the nasopharynx and throat to stimulate the mucosa of the throat and larynx, which can cause inflammation of the throat, including nasopharyngitis, pharyngitis, tonsillitis, adenoiditis, adenoid hypertrophy, laryngitis, throat pain, wheezing, coughing with sputum or less sputum, snoring, hoarseness and so on.

The upper trachea opens the throat and the lower trachea opens the lungs. When sinusitis occurs, on the one hand, nasal secretions enter the throat, causing inflammation of the throat, and can further spread downward, causing inflammation of the trachea and bronchi, coughing and other symptoms; on the other hand, the nasal cavity has the function of cleaning, filtering and disinfecting the inhaled air, and is the first line of defense against diseases.
When sinusitis occurs, this line of defense is destroyed. Dust and harmful substances in the air flow directly into the trachea and lungs, which are prone to diseases of the trachea and lungs. Clinically, obstinate tracheitis, bronchitis and bronchial asthma often coexist with chronic sinusitis, which is mostly related to allergic reactions caused by sinusitis.

Sinusitis, especially chronic sinusitis, has a large amount of pus in the nasal cavity. Sometimes the pus is blown out, sometimes it flows backwards from the nasal cavity, into the pharynx, swallowed by the patient and into the gastrointestinal tract. Toxic substances entering the gastrointestinal tract stimulate gastrointestinal mucosa and cause damaging changes such as congestion and edema. As a result, gastrointestinal function is affected, resulting in discomfort or pain of the gastrointestinal tract, gastric distention, dyspepsia, appetite loss, and mesenteric lymphadenitis (periumbilical pain, abdominal B ultrasound can diagnose).
Long-term loss of appetite will lead to malnutrition and developmental disorders in children (weak body, susceptible to colds, thin face, short stature). Because children do not take the initiative to blow, in most cases, nasal endocrine secretions flow backwards into the swallow and are swallowed into the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, the effect of chronic sinusitis on gastrointestinal tract in children is greater and more obvious.

Because the toxic and harmful substances in the purulent secretions of the nasal cavity and sinuses are absorbed locally or through the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in neurological dysfunction. The main symptoms are mental depression, fatigue, inactivity, dizziness or dizziness, headache, insomnia, mental deficiency, memory loss, emotional fluctuation, lack of concentration, restless sleep, molars, hyperactivity, and decreased academic performance.

As the saying goes, "Flickers are easy to break, and those who talk are easy to stain". Children are in the process of growth and development. Traditional Chinese medicine believes that children are immature Yin and Yang, so they are vulnerable to the influence of external factors leading to disease and dysplasia. Because of chronic sinusitis for a long time, purulent secretions are often swallowed into the gastrointestinal tract, resulting in loss of appetite, resulting in reduced food intake and reduced nutrition intake, which can not meet the needs of children's growth and development. If children do not meet the needs of growth and development for a long time, their growth and development will be hindered, and the manifestations of dysplasia will appear, such as weakness, susceptibility to colds, lack of spirit, inactivity, etc. Therefore, children with sinusitis should be highly concerned by parents and actively treated.
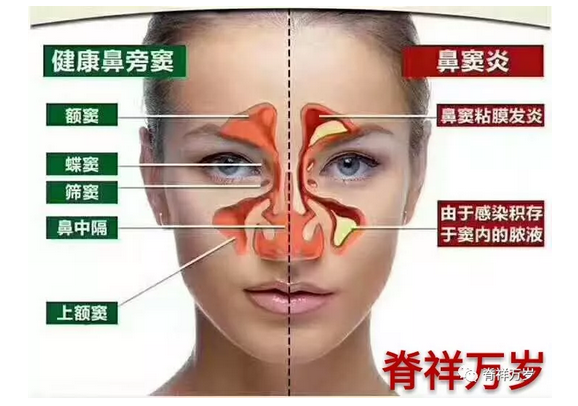
Why are children prone to sinusitis?